Perhaps all governments these days eventually do it, but one of the things that I’ve come to dislike most about our current government is the way they and their acolytes simply make stuff up. I could, I suppose, understand them not actually doing anything much. After all, they didn’t promise to do anything much.
But the endless spin, and stuff that is just made up, sickens me. Apart from anything else, I try to bring up my kids heeding the biblical injunction to honour those in authority over us. I don’t read that as suggesting people won’t disagree with those who hold office, but there is something quite sick about the political process – and perhaps about a society that tolerates this stuff – when so often one reads comments from senior ministers or the Prime Minister to which one can only explain to kids interested in such things that “they are just making it up”. We should expect much better than that.
I’ve written before about the current and former Prime Ministers’ dismissal of housing or conjestion problems as “quality problems” or “signs of success“. And there are the repeated claims that New Zealand’s economy is doing better than almost any other advanced country – a suggestion ably challenged in an article by journalist Graham Adams yesterday. But today, since it is the day Murray McCully leaves ministerial office after a very long period in ministerial roles in two governments. I wanted to focus on an unfounded claim in a recent speech to the New Zealand Institute of International Affairs by the outgoing Minister of Foreign Affairs.
He begins with an unexceptionable observation
The key feature of the past decade has been the rise of China, in terms of both our bi-lateral relationship, and as a regional and global power.
Not just of the past decade, but the past several decades.
And, as the Minister notes, there has been a big growth in bilateral trade (goods and services).
In my eight and a half years in this role I have seen our exports to China increase from around $2 billion to nearly $10 billion, and visitor numbers more than quadruple from under 100,000 to over 400,000.
But then he dramatically over-reaches
Had it not been for the dramatic expansion of trade and economic relations with China in the early years of the Key Government, New Zealand would have suffered a long and sustained recession, and all of the associated social challenges that we have seen in some European nations.
There is simply no support for this proposition anywhere in the rest of the speech.
The implication, of course, is that New Zealand has done well over the term of this government. But here is a chart of real GDP per capita for New Zealand and the United States, both normalised to 100 in the December quarter of 2007, just prior to the recession.
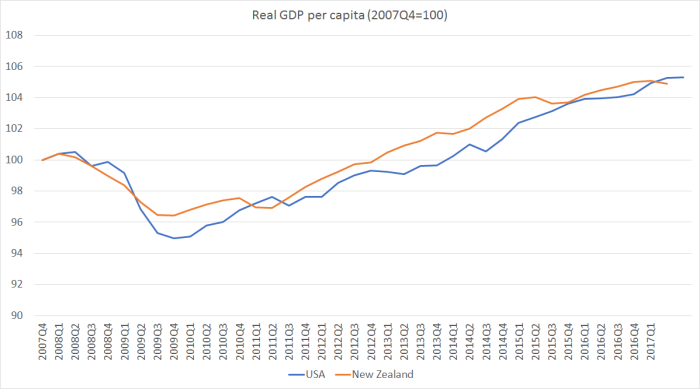
The United States, you will recall, was the epicentre of the financial crisis, and had a very nasty fall in house prices. The United States cut interest rates as far as they then thought they could go.
New Zealand, by contrast, had a relatively modest home-grown financial crisis (localised in the non-systemic finance companies), never reached the limits of conventional monetary policy, and had a much stronger fiscal position going into the recession than the US (or most other advanced countries had). Oh, and we the big bonus of a sharp fall in interest rates, as a country that had borrowed heavily from the rest of the world.
And yet look at the chart. The initial recession was certainly a little deeper in the US than it was here – but China wasn’t a significant influence on what was happening here in 2008/09. But then we had a double-dip recession in 2010.
For a couple of years it looked as though we might be doing a bit better than the US, at least on this metric, but even that optimistic possibility has now faded away. Over the nine years shown, real GDP per capita has grown almost exactly as slowly in New Zealand as it has in the United States (average growth rates of barely 0.5 per cent per annum). You’d have to know economic data pretty well to be able to tell apart the US and New Zealand lines for the last six years or so.
So we had a pretty nasty recession, which we took years to recover from. On some metrics – eg the unemployment rate – we still haven’t. And all that even though China took up a larger share of our exports. It is so even though in those “early years of the Key government”, China was a big source of demand driving activity in our biggest trade and investment partner, Australia.
The Minister seemed to be telling a trade and exports story – certainly those are the numbers he quoted. But here are exports as a share of GDP for the two countries, again back to December 2007.
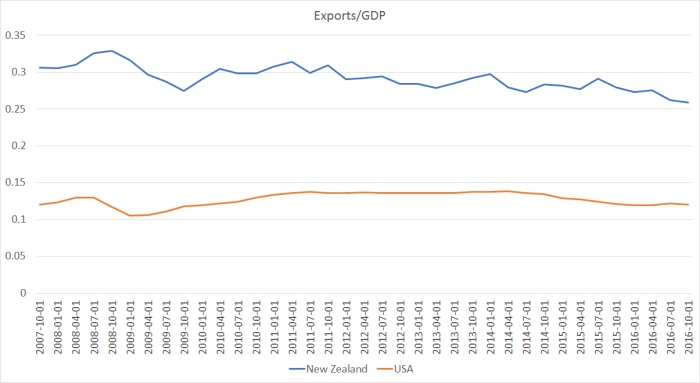
In both countries, exports took a hit during the recession – in the US’s case it was mostly volumes, while it our case much of it was prices (the fall in export prices). But, despite all that additional trade between New Zealand and China, our export share of GDP has fallen quite a bit over the last few years, while that in the US (always much lower, given that the US is a large country) has held remarkably steady.
Perhaps this fawning “China our saviour” line went over well when the Premier of China was visiting recently, but it really doesn’t amount to much at all. The country composition of our exports has changed – and for a couple of years perhaps high prices out of China for milk powder lifted farmer incomes – but as a share of the overall income, exports have been shrinking. We produce stuff (mostly bulk commodities), and someone buys it. In recent years, China has been a more important buyer – although Australia remains our largest export market – and the free trade market with China is likely to have been helpful, but it has hardly transformed our economic fortunes.
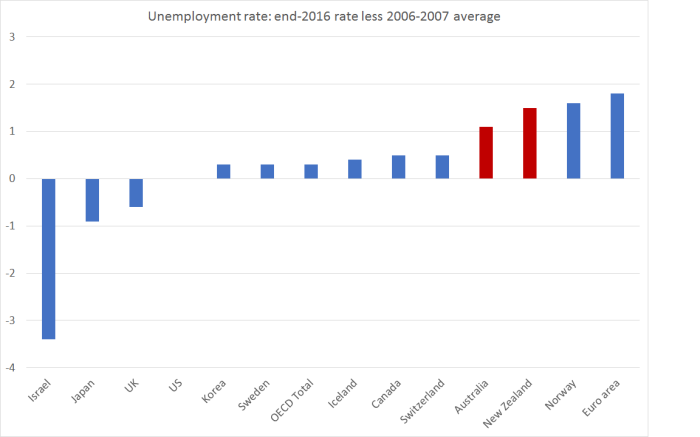
There are other differences between the US and New Zealand experiences. The US unemployment rate went up much more than ours did during the recession, but then came down much more sharply and is now a bit lower than ours.
But one striking difference over the last few years is in the estimated population growth rates.
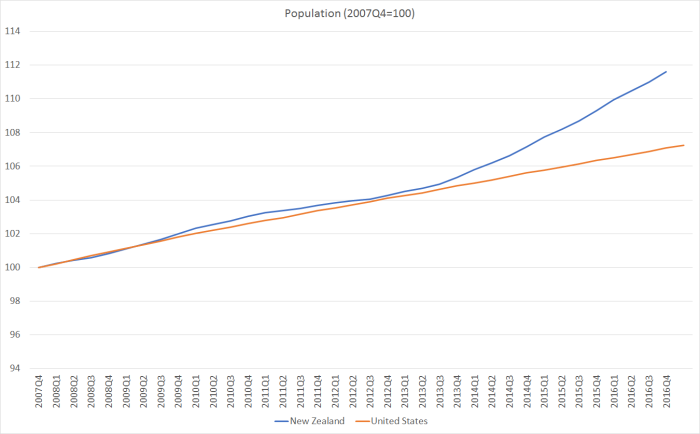
Overall, ours is a story of little or no productivity growth (none for the last five years), of an economy that – going by the headline statistics – seems increasingly inward focused, reliant on population-fuelled (and earthquake rebuild fuelled) domestic demand. And it is a pretty poor performance all round.
There are, of course, worse places among the advanced countries, and if that is all the Minister had wanted to say, no one could disagree. But instead he over-reached, suggesting that somehow we’d done well. We haven’t. And mostly that is down to our own choices – or, more specifically, those of the government in which Mr McCully has been a senior minister.