A speech appeared on The Treasury’s website the other day. It was, we were told, by Gabs Makhlouf, Secretary to the Treasury, and given as the closing address at a Productivity Hub Workshop last Friday. The Productivity Hub is a grouping of government agencies, hosted at the Productivity Commission
which aims to improve how policy can contribute to the productivity performance of the New Zealand economy and the wellbeing of New Zealanders
It is a laudable aim. I’ve been to a few of their events, and at times they’ve had some interesting and stimulating speakers. Whatever the event was that Makhlouf was speaking at, it has a very low profile – there is nothing about it on the Hub’s homepage, or anywhere else I can see. I’ve lodged a request for the papers and presentations.
I’m all in favour of pro-active release of material by government agencies, but I was a little curious why The Treasury chose to make this speech something on-the-record. Closing addresses usually seek to summarise and draw lessons from what has been heard at the conference/workshop. But in Makhlouf’s speech there is no reference to any of the papers that had been presented, or any of the material discussed at the workshop. Perhaps he just wanted to signal that he, Secretary to the Treasury, treats productivity as something important (on checking, I found that Treasury had also published his brief remarks to a couple of previous Productivity Hub events)?
Whatever the reason, when the Secretary to the Treasury – head of the government’s main economic advisory agency – talks about productivity, it should be worth taking note of. After all, presumably even now Treasury is in the process of pulling together the analysis and advice that will form the basis for their Briefing to the Incoming Minister (BIM) after the election. We might hope they will be (a) pointing out to the Minister of Finance that New Zealand’s productivity performance is woeful, and (b) offering a compelling narrative and set of recommendations for what might reverse that performance and enable New Zealand to deliver for its citizens the sort of standard of living they should reasonably expect. But on the basis of the Secretary’s latest speech, I wouldn’t be holding your breath.
Of course, one can’t expect any sort of fully-developed story in a few pages closing a workshop. But if there is (a) a sense of urgency, and (b) a well-developed set of policy proposals being worked-up, that should be clear in a speech of this sort. Neither is there.
Makhouf recognises that our productivity performance leaves something to be desired, but how is this for minimising the issue?
We are middle of the OECD pack at best in the amount of income we derive per hour worked, and we have made little or no headway on lifting our productivity performance rankings over the past 15 years.
There are 35 OECD countries now, and only 13 had real GDP per hour worked less than New Zealand’s in 2015 (most recent comprehensive data). And the only reason we are even near the middle of the OECD pack is because so many poorer countries have been allowed into the OECD. Every single one of the 11 new members in recent decades was poorer, and less productive than us, when they joined.
When we joined the OECD in 1973, it was a club of 24 countries. OECD data go back to 1970. And in 1970, our real GDP per hour worked was similar to that in France and Germany. These days, they have productivity 60 per cent higher than ours, and of those 24 countries only Portugal, Turkey, and Greece now have lower real GDP per hour worked than we do. In 1970, Turkey had GDP per hour worked less than half ours, while on the latest estimates it is now almost equal to us.
And while it is certainly true that “we have made little or no headway on lifting our productivity performance rankings over the past 15 years”, the story is much worse than that, as even the OECD highlighted last week. Here is their chart
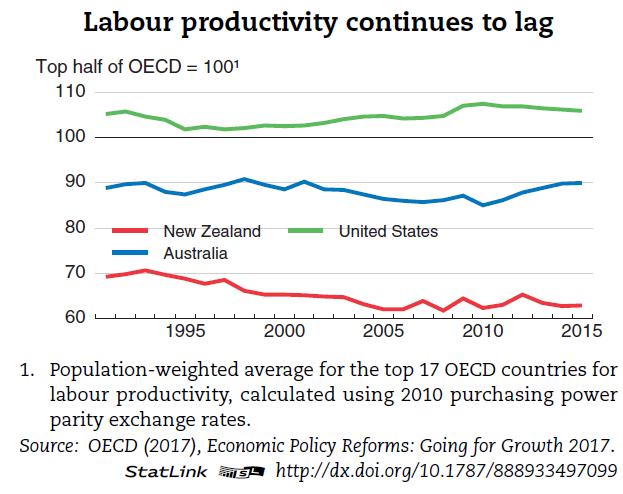
And this is mine, from a post a couple of weeks ago

In 47 years now there has never been a time when New Zealand has succeeded in narrowing the productivity gaps that have opened up between us and other advanced countries. At best, we’ve gone sideways in some periods.
And if Makhouf understates the severity of the problem, he overstates any signs of progress
Our understanding of New Zealand’s productivity performance is improving, thanks to a wealth of information that has recently been released including as a result of the Productivity Commission’s report Achieving New Zealand’s Productivity Potential, the OECD’s New Zealand Country Study and Going for Growth, and the Treasury’s He Tirohanga Mokopuna. (That last one is a cracking read, by the way.)
Really? The Treasury report he refers to was their long-term fiscal report, and I’m genuinely puzzled as to how he thinks that (useful) report advances our understanding of the productivity underperformance. The Productivity Commission piece, which I wrote about here, was an interesting effort, and did represent a step forward in some areas (including the treatment of immigration policy) but it has hardly galvanised the nation – or even, as far as I can tell, official Wellington. As for the OECD’s report, surely Makhlouf was just being diplomatic – the OECD chief economist was at the workshop – rather than seriously suggesting that they have a compelling narrative to explain New Zealand’s underperformance and, thus, a solid model to use in proposing remedies?
Makhlouf goes on
Our challenge now is to keep building the momentum of progress and turning our growing understanding into action that lifts our productivity performance.
But where is the progress at all? Where, specifically, is the evidence that Treasury – or other government agencies – are any closer to credible answers?
Makhlouf set out what might have been an interesting marker
As I mentioned, we have seen little improvement on where we rank among OECD countries for productivity, yet we have been told that we have world-leading settings.
This raises a few questions for me. ….. Or could it in fact be that New Zealand’s world leading economic and policy settings aren’t so world-leading anymore?
I’m not sure who really thinks of New Zealand policies are being “world-leading” these days. In some areas, perhaps they are. In other areas, we score quite badly. But I’d have thought a fair overall description would probably be ‘no worse than the typical OECD country’.
Sadly, Makhouf doesn’t really do much to develop his tantalising question.
‘World-leading’ is always evolving. Looking back through history, Rome, China, India and the United Kingdom have all at times been world leading economies, just as the United States is today. So while some things will continue to hold for productivity and incomes, we need to make sure we are not working towards something that used to be world-leading, but is no longer so. It’s also likely that what’s world-leading will vary by country so it’s not a recipe that we can simply copy.
Surely all this confuses great power status – not unrelated to economic strength typically – with world-leading (economic) policy settings? After all, he could have noted that 100 years ago, New Zealand looked pretty world-leading – not as a “great power” but as one of the very richest and most productive nations on earth. Nor am I really quite sure how “what’s world-leading will vary by country” makes much sense, unless he is saying – in which case I agree – that in thinking about diagnosing New Zealand’s problems and offering remedies to policymakers we need to think hard about the specifics of New Zealand’s situation. It isn’t clear that the OECD (at least) has really done that.
But it isn’t clear that Treasury is really doing so either. Because Makhlouf devotes the rest of his remarks to
five factors that the Treasury believes always matter: skills, connections, markets, resources and rules.
Any micro-focused policy agency almost anywhere in world could trot out that list
Of skills
The Treasury believes that opportunities remain to lift skills and resilience in the workforce, and it’s important that those opportunities are pursued.
No doubt, but it doesn’t seem particularly persuasive that gaps here are big part of the 45 year story of underperformance, when the OECD adult skills data suggests New Zealand workers already have among the highest skills of any in the OECD.
Of connections
Connections matter, in particular people-to-people connections. And as Asia continues to dominate economic activity, perhaps those types of connections – ie, relationships – matter more than ever. Improving connections can help to improve the flow of people, capital, trade and ideas that contribute to productivity. Strong people-to-people relationships build confidence and understanding and promote learning. They help our businesses to identify capabilities that will help them improve their productivity and ultimately compete and succeed in both domestic and global markets.
I suspect this is some sort of code for “keep on having lots of immigration”, but it isn’t terribly specific. And as a reminder, with rare exceptions, Asia isn’t the home to the richest or most productive economies. But again, with hugely high (by international standards) rates of non-citizen immigration, did Makhlouf and Treasury have anything remotely specific in mind?
He gets a little more specific on “markets”
In the Treasury’s view we need to continue to lift the competitive intensity of the New Zealand economy. The pressure of competition pushes firms to be more productive, for example by innovation to improve quality or cut costs. We need to ensure our markets are as competitive as possible by reducing the barriers to entry, including for imports (whether in goods or services), or by regulating the price and quality of goods and services in markets where there is little or no competition, such as in our telecommunications and electricity markets. And we need to maintain the effectiveness of competition laws and institutions. If we want competitive markets and the productivity gains they bring, we have to ask ourselves: what are the regulatory barriers preventing competition and what can we do about them? How bold do we want to be to invite competition?
It isn’t really my area, but if there is useful stuff to be done in this area how plausible is it that it can materially explain 45 years of relative economic decline? Say what you like about competition in New Zealand now, but in almost all areas there is a great deal more than there used to be.
Then he moves onto natural and physical resources. Here he includes housing.
Our natural and physical resources are next. One of the most high profile issues we’re examining in New Zealand – housing – illustrates how these resources are a significant factor in productivity. We are all aware of issues in house price growth in Auckland and the inefficiencies in our use of land which are proving to be a bottleneck in New Zealand’s growth and productivity.
I’m not sure there is really any evidence for this proposition. If there is, in a New Zealand context, perhaps The Treasury could publish it. Dreadful as our housing policies are, when the city that is worst affected by them has (a) had very rapid population growth, and (b) has a very small margin by which productivity exceeds that in the rest of country, it suggests that overseas studies – on places like San Francisco and New York (which have had little population growth, and very high productivity margins) – may not be of much direct relevance here.
Still on housing
the degree of its affordability or unaffordability is a product of our entire urban development chain and of multiple interacting areas of policy. We’re considering these issues holistically, as well as particularly how land owners capture the economic rents and potentially magnify the problems. We see the concept of competitive land markets as an important part of the way forward.
Surely if there is something there, it could have been written a great deal more simply? And portentous words about “the concept of competitive land markets as an important part of the way forward” almost make a mockery of people priced out of home ownership right now.
In some areas, I’m not sure Makhlouf really knows what he is saying
At the moment, it can be argued that too much of our natural resource use is determined by incumbency rather than most efficient use.
Does inumbency here mean “the person who owns it”? But, surely, land is our greatest natural resource. Mostly, it is pretty freely tradable. Anyone with a better, more profitable use, in mind can surely make an offer? Or (but surely not) is the Secretary perhaps a bit worried about private land ownership?
Actually, despite what he said, he seemed to be mostly talking about water rights and pollution. What he says on water sounds sensible
To use water as an example, the ‘first-in first-served’ approach to water allocation means it may not always be allocated to the highest value use, and the current system lacks sufficient incentives for use to move to a higher value one. The Freshwater Allocation Work Programme is considering options that could be more appropriate to ensure that we are getting the best use of our water resources.
And I’m sure there are some real issues around pollution too. But when he says
Better rules around use and around pricing externalities such as pollution are critical to making best use of resources and are likely to be key to promoting significant diversification of the economy and contributing to an improvement in productivity.
I think he makes it sound all too easy. For example, it is all very well to talk of water pollution arising from more intensive dairying, or indeed of the implications for carbon emissions, but without a great supporting analysis it sounds a lot like feel-good rhetoric to suggest that restricting such industries is likely to be significant in lifting overall productivity in the economy. What channels, one wonders, does the Secretary have in mind?
His final category was rules
The making of rules and regulations – whether by central or local government or even by self-regulated occupational groups – has an impact on productivity. All rule-makers help shape the environment in which investment, enterprise, and job creation is either promoted or limited. Rule-makers in the public sphere have a double responsibility: to ensure effectiveness in public spending and decision-making, and to provide the best possible regulatory and policy settings.
Hard to disagree really. But is this really the best the Secretary to the Treasury – an agency with key responsibility for regulatory review policy – can do on the contribution of New Zealand regulation to productivity? There isn’t even an attempt to draw some of his points together, and note that (for example) well-intentioned but flawed rules help explain the absence of a well-functioning market in urban and peripheral land.
Overall, there is no sense of urgency, and no hint of any fresh insights either.
Makhlouf ended his speech this way
We need to continue to test our assumptions about what does and doesn’t work, and to apply new things where they make sense. I know there’s a lot of willpower and brain power here to ask questions, find solutions and take actions to raise New Zealand’s productivity.
Of course, it is elected politicians, not officials, who would get to “take actions to raise New Zealand’s productivity”. Sadly, despite the approaching election, there is little sign among any of them – or those competing to take their place – of much will to change, or much interest in attempts at serious answers to decades of decline.
Should there be more urgency? I’d have thought so. There has been plenty of talk in the last few years of New Zealand and Australia relative economic performance. Australia is our biggest trade and investment partner, and of course historically an outlet for New Zealanders pursuing the far higher incomes typically on offer there. It is certainly true that the Australian labour market has been cyclically weak in recent years, even more so than ours. But here is the latest update of labour productivity in the two countries (in NZ, using an average of the two GDP measures, and an adjustment to hours worked for the break in the series last June). The chart is indexed to 2007q4, just prior to the recession, but remember that even then we were well behind Australia (incomes and productivity levels)
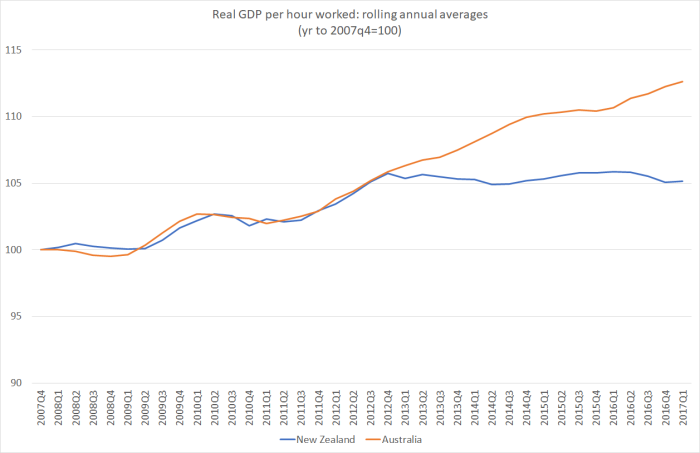
As it happens, Makhlouf’s appointment as Secretary to the Treasury was announced on 28 June 2011. We’ve had barely any productivity growth since then (none for the last five years). That, of course, isn’t directly his fault, but one does have to ask whether The Treasury under his stewardship has even once put forward a compelling set of policy proposals to end even this multi-year drought, let alone to reverse the 45 years and more or relative decline. On the basis of this latest speech, we shouldn’t be very hopeful of what they might have to offer a government formed later this year.
“And as a reminder, with rare exceptions, Asia isn’t the home to the richest or most productive economies”
I really do have to wonder at the consequences to our productivity (and innovation) as a result of sourcing large numbers of immigrants from some of the lowest productivity countries (India or the Philippines for example); massive labour inputs and junk results.
Excess (and cheap) labour will also tend to lower productivity increases by reducing capital, mechanical and systems improvements incentives.We need to end or drastically cut our intake of unskilled third world labour. The so called family reunion category and sleazy “mail order bride” needs a good hard look at as well.
LikeLike
My friend Bushan once said “they have brought in the wrong Indians”. In the UK and the USA expanding exporting businesses disproportionately are owned by families originating in India (often Gujarati). In NZ we have about forty Chinese in the investor category to each Indian.
LikeLike
I wonder what effrect Kiwisaver has had in the past decade? There seems to be now about $40bn plus in “savings” and from my own experience most is invested offshore. Not in productive capital in NZ. And has the saving displaced spending that would have driven GDP and incomes higher in the past decade?
The graph of decline in relative standards since 1970s shows the greatest decline in 1970s – we were living in a fools paradise? Then a further 10% decline from mid-80s through to early 2000’s – a fool’s neoliberal solution? Finally stablising from 2005 onwards? Perhaps we have learnt something?
LikeLiked by 1 person
A taboo topic that needs to be explored much further – doesn’t get much airing from the lever-pullers who find it easier to cry out NZ needs more imported foreign capital to facilitate growth and productivity
A large proportion of the National Super fund is invested offshore creating jobs in those recipient destination locations – and now you say a further $40 billion in kiwisaver
It seems nuts to be exporting capital to unknown destinations faster than we can get foreign capital to come here and do goodness only knows what. The star-chamber elite blue-bloods scream out for more but never provide any examples of the benefits gained from imported capital and remain absolutely silent on the reverse drain of exporting capital
LikeLiked by 1 person
The OECD published a report last year in which they show that productivity growth has generally slowed down worldwide in both developed and developing countries.
The most interesting bit of information in that report for me was that productivity growth during the first decade of the 21st century was driven almost exclusively by the 100 most advanced/productive firms in both the manufacturing and services sector, with the divergence being more pronounced in the services sector (page 18).
Of course, their time series stops shortly after the financial crisis which seems to have caused a significant part of the divergence. It would be interesting to know how things have developed since then.
Report: http://www.oecd.org/publications/the-productivity-inclusiveness-nexus-9789264258303-en.htm
LikeLike
Thanks. The other problem with the fascinating firm-level analysis is that there is usually almost no real historical data so that, extraordinary as these statistics seem, there is little way of knowing whether it was the way productivity has always advanced.
From a NZ perspective, of course, some of this stuff should be less relevant, because our overall level of productivity is so far from the global frontiers. We could go for several decades mostly just catching up.
LikeLike
If competition is the main driver of innovation / productivity, policy options in this area could be quite interesting (even if an unlikely vote winner). I think you mentioned once the relatively high number of occupations in NZ requiring ‘licenses’ – no doubt mainly in the service sector which seems to be dragging down the numbers i.e. the trade v non-trade debate..
LikeLike
and meanwhile the govt is in the process of adding yet more occupational licensing restrictions, this time for (of all things) social workers
LikeLike
If you’ve seen this week’s economist, which focuses on Germany, you may have noticed that the German economists credit wage restraint for their export success. I thought this was interesting, and a bit counterintuitive. They thought the wage restraint somehow led to an increase in national saving, by some mechanism that wasn’t clearly spelt out. Which doesn’t clearly fit with standard economics, but when you think about it a lot of high-savings export powerhouses are good at wage restraint. I was left wondering whether NZ’s fascination with high minimum wages was yet another factor inhibiting productivity.
LikeLike
I guess wage restraint is akin to an exchange rate depreciation which works, largely, by lowering the (relative) cost of domestic resources. China’s export growth phase was powered partly by an artificially low real exchange rate – a strategy arguably still being adopted by Singapore and Taiwan.
LikeLike