As New Zealand readers won’t be able to avoid knowing from the blanket media coverage, today is the fifth anniversary of the most destructive of the thousands of earthquakes that have hit Christchurch and its neighbouring areas since September 2010.
Christchurch is “home” to me. I haven’t lived there for decades, and don’t suppose I will again. But almost all my wider family live there, and my ancestors for 150 years or more have lived in and around Christchurch. Many of my family were, and are, badly affected by the 22 February quake: my elderly parents managed to get down the damaged stairs of their multi-storey apartment block, but never even got inside the building again. The church where they had been raised, and married, and where several generations had been buried from, lay in ruins.

On Friday, presumably to mark the anniversary, the Reserve Bank released an issue of the Bulletin looking at how the economy of Christchurch and the Canterbury region has fared in the years since the worst of the quakes (it is billed as “The Canterbury rebuild five years on”, but is mostly about economic activity in Canterbury, of which of course the rebuild is a significant, if temporary, new part). The article builds on an earlier one along much the same lines published in September 2012.
There is a range of interesting material in the article, as well as a few things that read oddly. For example, the authors note on several occasions that “the bulk of commercial building reconstructions has yet to start”, which seems to defy the evidence of the senses (there has been a lot of building going on in and around the central city in the last year, public and private, and a lot of “for lease” signs on the new buildings), unless the Bank is much more optimistic than most people seem to be on just how large a CBD Christchurch is likely to have in the next decade or two. And the authors include this chart, using SNZ data, suggesting that retail sales in Christchurch have been much stronger than in the rest of the country
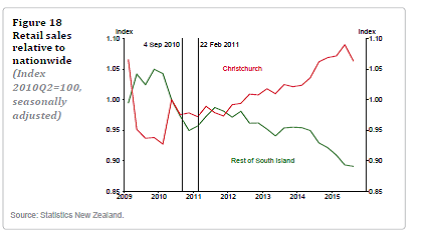
Which seems a little odd, since population growth has lagged behind that in the rest of the country. Using the SNZ subnational population estimates, between June 2010 and June 2015 populations are estimated to have grown as follows:
| New Zealand | 5.60% |
| Canterbury regional council | 3.30% |
| Christchurch city | -2.30% |
| Christchurch city + Selwyn and Waimakariri | 2.60% |
Even allowing for the lower unemployment rate in Canterbury than in the rest of the country, it would seem surprising if retail sales per capita had grown so much more strongly than in the rest of the country (estimated retail sales 6 per cent faster – see chart – and population growth perhaps 2 to 3 percentage points slower.
But in commenting today, I didn’t want to focus on the fine details of a useful article. Instead I wanted to comment briefly on three thoughts that struck me as I read.
First, in an article written by officials in a government agency, the authors are quite constrained in what they will have felt able to say about the rebuild process and the role of central government in it. It is perhaps useful to read the Bank’s article alongside, say, the article in this week’s Listener. And the Bank’s primary focus is, of course, on resource pressure issues, not the effectiveness or otherwise of the rebuild process. But silence on some of these matters risks being read as endorsement. I’ve noted already the comment about the commercial rebuild process, but if the authors are right that there is a lot more to come, perhaps it is worth pondering what role central government has played in slowing down the process. For example, the use of compulsory land acquisition powers, in pursuit of some official vision of what the city centre “should look like”, which will have contributed to much higher than necessary land prices in the central area. Or the uncertainty which central government has created by promoting (almost certainly uneconomic) so-called anchor projects, and then making almost no progress on them – leaving private investors considering projects that would sensibly locate close to the “anchor projects” in limbo.
Second, a couple of charts in the article prompt a “what might have been” thought about the entire economy. Some have argued that the New Zealand economy would have performed much more poorly over recent years without the repair and rebuild process. If anything, I think the opposite is true. Right from the early days following the earthquakes, the Reserve Bank was focused on the size of the rebuild expenditure, and associated pressure on resources, that was to come over the following few years. As probably the largest investment programme in New Zealand (share of GDP) since the Think Big projects in the early 1980s, and with a very domestic spending component to it, it was quite right for the Bank to focus on those issues and risks. But, with the benefit of hindsight, I think that doing so helped leave the Bank more reluctant than it should have been to have cut the OCR as the record of persistently low inflation kept building up. The sentiment was often along the lines of “it might be low right now, but it can’t last – look at all those resources pressures to come in Christchurch in the next few years”.
If the economy had been fully employed, the repair and rebuild process would inevitably have had to “crowd out” some other economic activity – most probably from the tradables sector. In fact, we’ve had an underemployed economy throughout the last five years and could, with hindsight, have done with more demand, which would have generated more economy activity, less unemployment and a bit more wage and price inflation. Without the spectre of the rebuild programme, there might have been more chance of it being allowed to happen.
Part of what I’m talking about is captured in these two charts from the Bank’s article.
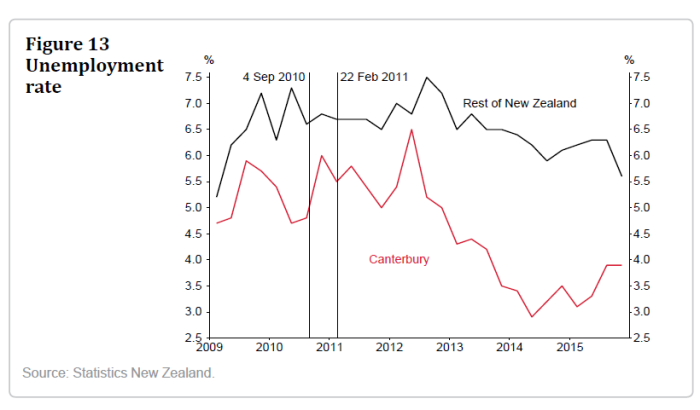
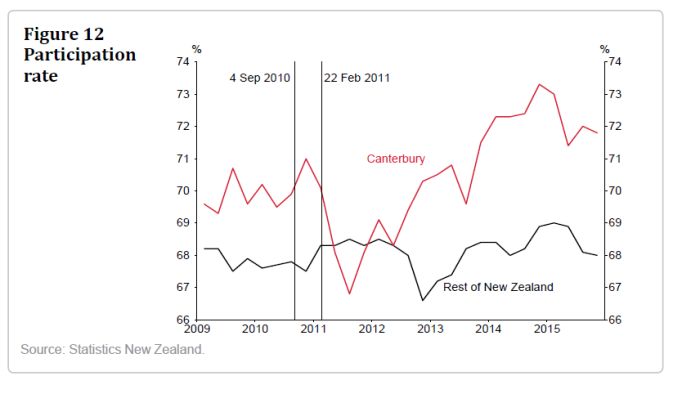 The labour market in Canterbury has been materially stronger than in the rest of New Zealand. Even pre-quake, the participation rates were higher and the unemployment rates were lower (probably partly reflecting different demographics), but both gaps widened further in Canterbury’s favour as the demand/activity associated with the rebuild really got underway from 2013.
The labour market in Canterbury has been materially stronger than in the rest of New Zealand. Even pre-quake, the participation rates were higher and the unemployment rates were lower (probably partly reflecting different demographics), but both gaps widened further in Canterbury’s favour as the demand/activity associated with the rebuild really got underway from 2013.
With a lower OCR over the last few years, and the associated lower exchange rate, the whole of New Zealand could have enjoyed a milder version of this sort of buoyant labour market. The intense focused nature of the rebuild “shock” probably always meant that the Canterbury market, at peak, would be tighter than that in the rest of the country, but the rest of the country simply could have done materially better. Demand makes a difference, and monetary policy can either hold back or stimulate demand.
Had the demand been there in the rest of the country to generate stronger labour market outcomes, there would have been inflation consequences. But that would have been a good thing, not a bad one. Recall that inflation has been well below target for years. And as the Bank notes
In real terms, wages in Canterbury have increased by about 8 percent since the earthquakes, whereas wages outside of Canterbury have increased about 6 percent in real terms.
Hardly of a magnitude – 2 percentage points different in total over five years – that, repeated nationwide, would have been sufficient to have blown the inflation rate back through the upper end of the target range.
One can’t simply mechanistically translate one region’s experience into that for a whole country, but the simple comparisons outlined here point in the direction of what went wrong with monetary policy management in New Zealand in the last few years. With a huge non-tradables demand shock (which, in macro terms, is what the rebuild represents) New Zealand should not have had any great difficulty keeping inflation up around target in recent years – indeed, one could, if so inclined, have mounted an argument for it to have been a little higher for a few years, reflecting the intense one-off nature of the shock).
My final set of thoughts, rather more speculative, is around the longer-term health of the Christchurch economy. The Bank repeatedly describes the Canterbury economy as being “resilient” (including in its press release) , but if anything I came away from the article more sobered and worried about the future of Christchurch than I had been. In internal debates in the immediate wake of the earthquake, I was always one of those who pushed back against the idea that there would be a wholesale exodus from Christchurch, from which the city would never recover etc. Apart from any other arguments, between risks of tsunamis, volcanoes, earthquakes, and floods where in New Zealand was really much safer in the longer-term? And there hasn’t been such an exodus – indeed, the population of greater Christchurch is higher it was in 2010.
But there always was Professor Ilan Noy’s work suggesting permanent adverse effects (population and economic activity) from past overseas natural disasters. Noy is now at Victoria University and is listed as a co-author of the Reserve Bank’s article.
The Christchurch economy has historically drawn strength from a number of areas. There was a large manufacturing sector, with a significant high-tech and export orientation. That sector hasn’t been materially affected by the earthquake and subsequent rebuild process – but then the overall manufacturing sector (especially outside the construction-related bits) has been performing poorly (per capita manufacturing value-added is now only around 80 per cent of what it was in the early 2000s). Christchurch has also built on the large rural hinterland – which is still there, and probably more intensive than ever as vineyards (to the north) and dairy displace sheep.
But Christchurch has also become a reasonably significant location for export education (one of the worst sets of fatalities was a English language school for foreign students) and some combination of tourist destination and gateway to the picturesque South Island. I’ve never been entirely confident that tourism is a robust basis for long-term high advanced country living standards (it isn’t tourism – much more of it than New Zealand has – that makes France or the UK prosperous), but some of the charts in the article were sobering.
Guest nights
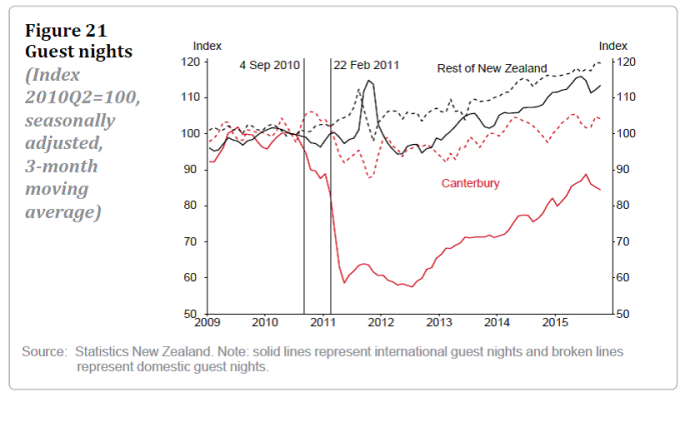 International numbers are recovering, but there is a very long way to go. Perhaps not too surprisingly (cause and effect) hotel capacity in Canterbury is only about 60 per cent of what it was.
International numbers are recovering, but there is a very long way to go. Perhaps not too surprisingly (cause and effect) hotel capacity in Canterbury is only about 60 per cent of what it was.
Or international student numbers, where there has been no recovery at all (although I gather the picture for graduate students is a little more encouraging).
 The chart for foreign fee-paying school students is even weaker.
The chart for foreign fee-paying school students is even weaker.
The Bank ends its article noting
In particular, activity in the tourism and education sectors remains markedly below pre-quake levels. Without increased activity in other sectors, the labour market in the region could see a reversal of the improvement that has occurred in recent years, leading to reduced participation, higher unemployment and outward migration.
No doubt activity in some of those tradable services sectors will recover further at some point, but how far and how quickly? In some way’s Christchurch’s tradables sector plight probably isn’t a million miles out of line with the experience of much of the rest of provincial New Zealand, which has struggled to cope with the effects of a persistently high exchange rate, out of line with the longer-term real economic fundamentals. In aggregate, economic activity in Christchurch has been held up by the repair and rebuild spending, but that won’t last for ever, and is no longer an impetus for growth (the volume of activity having now levelled off). “Buoyant” might have been a better description than “resilient”.
Like many places in New Zealand, Christchurch is a nice place to live, but as the rebuild phase passes, there must be doubts about the ability of economic activity in the area to support high incomes for a growing population. It is a concrete illustration of the more general need for a reorientation of policy in directions that would generate a lower real exchange rate – a stronger competitive foundation – for at least a decade, to help unwind the adverse effects of the last decade: successive non-tradables shocks, exacerbated by policy mistakes, resulting in an exchange rate too high, it appears, to support, much growth in the tradables sector.
As I noted, the Reserve Bank authors will have been constrained in what they could say. The same constraints don’t apply to Professor Noy. Perhaps a journalist could consider approaching him, and inviting him to elaborate on his thoughts on the Canterbury economy and the apparent fragility of its rebuild-fuelled activity?
Are you forgetting that Bollard cut interest rates by 50 bps from 3 to 2½%, in response to the 2011 ChCh earthquakes, not in response to global events
The question is who were the beneficiaries of Bollard’s rate cut. Time and events have shown that one single rate cut became Bollard’s “helicopter Ben’s” moment as Auckland went on a spending spree while central government sat back and watched, while (many) Christchurch residents have had their lives upended and remain so to this day
Headline – Thursday Mar 10, 2011
All the major banks today moved to slash interest rates after the Reserve Bank said it was cutting the Official Cash rate by 50 basis points to 2½% following last month’s devastating earthquake
http://www.nzherald.co.nz/business/news/article.cfm?c_id=3&objectid=10711147
LikeLike
No, I’m not forgetting – but should have mentioned – that cut. But the cut probably needed doing anyway (the first tightening cycle had started in 2010 and by Feb 2011 there was already a fair amount of unease internally about whether it had ever been necessary. Read the subsequent MPSs and OCR reviews with their constant focus on the resource pressures that the rebuild would entail. I’m not critical of that focus, just arguing that it helps explain why the Bank was reluctant to take OCR below 2.5% – and so ready to tighten in 2014 – even as the overall inflation climate remained v weak.
LikeLike
“For the young man with moderate capital, “the Canterbury Settlement in its first few years presented opportunities unsurpassed in the whole history of British colonisation”
…
Not sure who said that. It comes from the Mobil Guide to NZ, but I suppose that would be a good first shock (or kick-start). Lately we seem to have developed a real estate economy and the earthquake has exposed the hollowness of it all?
LikeLike
I’ve been wondering about the long-term effects of the next movement on the alpine fault on dam reservoirs? I wonder if all reports are publicly available?
LikeLike
**I wish anyone reading Michael’s blog from Christchurch all the best for what is likely a day of reflection but with an eye on the future**
It is interesting that in this instance, demand followed from a (tragic) event outside the economic system and presumably such demand would have occurred regardless. Whether a stable/falling OCR profile since 2011 (relative to what has been in place) would have lowered the exchange rate, boosted confidence, raised expectations of future incomes, propelled demand forward and driven a flow of resources into productive activity, is really a counterfactual scenario that is anyone’s guess. Certainly worth pondering but it seems to me the link between changes in official rates and changes in demand – both here and abroad – is currently less linear than it once was. Agree that “demand makes a difference” but the question of ‘what’ determines changes in aggregate demand and the nature of such demand (e.g. flows versus stock considerations), is, to me at least, currently somewhat perplexing.
LikeLike
Do you have in mind any cases where lower official interest rates appear to have (causally) lowered demand and economic activity?
Recall, that with a huge exogenous non-tradables shock boosting demand, we should have found it easier than any country – Norway eg! – to have kept inflation up near target.
LikeLike
No example just a question of whether the magnitude of the cut in official cash rates from peak to trough had/is having the expected impact on demand and whether a further reduction would have had a material marginal impact given the aforementioned. In the case of NZ, the rate rises were unwarranted but the broader question over changes to the ‘transmission mechanism’ remains open (at least to me). For example, given where usd/gbp/eur/jpy rates are and have been, what OCR level would have brought about a depreciation of the NZD sufficient to kick start a resource shift to tradeable activity? Hard to know but to your point the other day, communicating a ‘return of the normal’ might be a major headwind.
LikeLike
It got quite scary when the RBNZ was determined to slow down inflation caused by a Christchurch rebuild. It is rather unbelievable that Wheeler would have even considered a disaster recovery as a major cause for a lift in interest rates. Why would anyone intentionally try to slow down a disaster recovery? He should have paid more attention to the other departments, like immigration that reacts with bringing in more foreign workers to plug the gap or of the many many foreign construction companies that would have access to cheaper materials and cheaper labour that would have also tendered for repair and rebuild jobs.
LikeLike
There is a logic to it. We didn’t want the one-off pressures spilling over into a generalized rise in inflation and inflation expectations which might then have been very hard to reverse later on. But it might be reasonable to have argued that (a) we should have focused on current core inflation measures, and reacted to possible upside pressures only when they were apparent, and (b) in any case, should have been happy seeing inflation in the upper half of the target range for some time, taking a risk that those specific relative price changes would not spill into expectations etc.
Personally, I’m not overly critical of the RB in-principle handling of the rebuild per se – I was actively involved in shaping how we thought about it – but I do think that the size of that shock helped create a climate in which the Bank became less likely (inappropriately so) to react to persistent downside surprises in actual inflation. The shock helped lead both Governors (Bollard and Wheeler) astray, at a time when – as I noted to QC above – it should have been easier for NZ to see inflation at or a bit above target than it was for any other advanced country (none of whom had such large exogenous boosts to spending and activity).
LikeLike
Commercial rebuild a WIP – that is my understanding. Presumably experts able to compare known/estimated insurance payouts with consented building values, or other measures, and aren’t just guessing.
Retail sales being higher in Chch – doesn’t surprise me, I imagine plenty of people have been refurbishing their properties as their houses are fixed/rebuilt. And I assume plenty of that spending will appear in retail sales. Might be interesting to see what happens next as I understand the residential rebuild has passed it’s peak.
LikeLike
Re retail, I think that story made sense to me in the early years of the repair/rebuild process – after all, damaged contents often needed complete replacement. It is more surprising this many years on, even allowing for the new houses being built (after all, in Auckland – 40% of the non-Chch population – there is a big boost to retail sales per capita from new immigrants, arriving with generally a fairly limited stock of consumer durables). Perhaps it is right, or perhaps the population estimates the retail numbers are based on are wrong?
LikeLike